[ad_1]
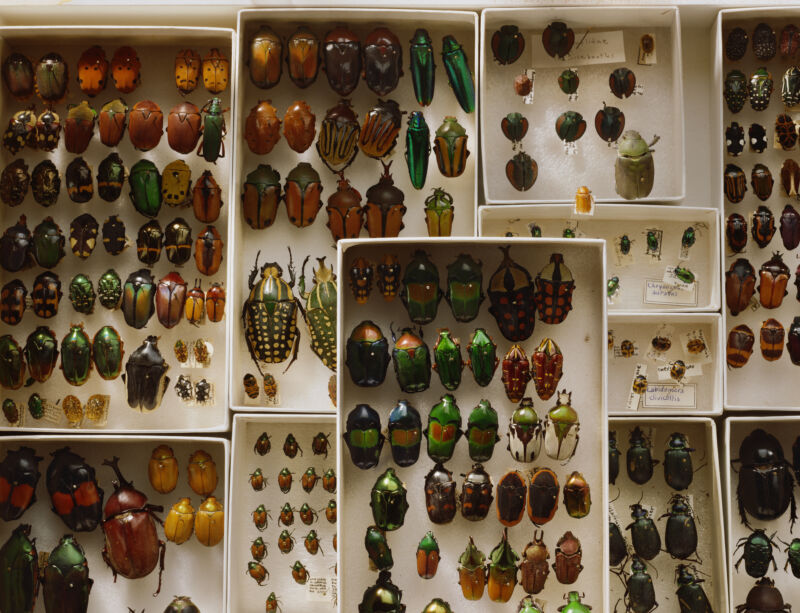

Caroline Chaboo’s eyes gentle up when she talks about tortoise beetles. Like gems, they exist in myriad vivid colours: shiny blue, pink, orange, leaf inexperienced and clear flecked with gold. They’re members of a gaggle of 40,000 species of leaf beetles, the Chrysomelidae, one of the vital species-rich branches of the huge beetle order, Coleoptera. “You might have your weevils, longhorns, and leaf beetles,” she says. “That’s actually the trio that dominates beetle range.”
An entomologist on the College of Nebraska, Lincoln, Chaboo has lengthy questioned why the dominion of life is so skewed towards beetles: The tough-bodied creatures make up a couple of quarter of all animal species. Many biologists have questioned the identical factor, for a very long time. “Darwin was a beetle collector,” Chaboo notes.
Of the roughly 1 million named insect species on Earth, about 400,000 are beetles. And that’s simply the beetles described to date. Scientists usually describe 1000’s of recent species annually. So—why so many beetle species? “We don’t know the exact reply,” says Chaboo. However clues are rising.
One speculation is that there are many them as a result of they’ve been round so lengthy. “Beetles are 350 million years previous,” says evolutionary biologist and entomologist Duane McKenna of the College of Memphis in Tennessee. That’s quite a lot of time through which current species can speciate, or break up into new, distinct genetic lineages. By means of comparability, trendy people have existed for under about 300,000 years.
But simply because a gaggle of animals is previous doesn’t essentially imply it should have extra species. Some very previous teams have only a few species. Coelacanth fish, for instance, have been swimming within the ocean for roughly 360 million years, reaching a most of round 90 species after which declining to the 2 species recognized to be dwelling at present. Equally, the lizard-like reptile the tuatara is the one dwelling member of a as soon as globally numerous historic order of reptiles that originated about 250 million years in the past.
One other potential rationalization for why beetles are so wealthy in species is that, along with being previous, they’ve uncommon endurance. “They’ve survived no less than two mass extinctions,” says Cristian Beza-Beza, a College of Minnesota postdoctoral fellow. Certainly, a 2015 research utilizing fossil beetles to discover extinctions way back to the Permian 284 million years in the past concluded that lack of extinction could also be no less than as necessary as diversification for explaining beetle species abundance. In previous eras, no less than, beetles have demonstrated a placing capacity to shift their ranges in response to local weather change, and this will likely clarify their extinction resilience, the authors hypothesize.
[ad_2]


