[ad_1]
The international monetary and financial disaster resulted in many countries chopping again on all types of public spending, and but navy spending continued to extend. Solely in 2012 was a fall in world navy expenditure famous — and it was a small fall. How would continued spending be justified in such an period?
Earlier than the disaster hit, many countries have been having fun with both excessive financial progress or far simpler entry to credit score with none data of what was to come back.
A mixture of things defined elevated navy spending lately earlier than the financial disaster as earlier SIPRI studies had additionally famous, for instance:
- Overseas coverage targets
- Actual or perceived threats
- Armed battle and insurance policies to contribute to multilateral peacekeeping operations
- Availability of financial assets
The final level refers to quickly creating nations like China and India which have seen their economies growth lately. As well as, excessive and rising world market costs for minerals and fossil fuels (a minimum of till just lately) have additionally enabled some nations to spend extra on their militaries.
China, for the primary time, ranked quantity 2 in spending in 2008.
However even within the aftermath of the monetary disaster amidst cries for presidency lower backs, navy spending appeared to have been spared. For instance,
The USA led the rise [in military spending], but it surely was not alone. Of these nations for which knowledge was accessible, 65% elevated their navy spending in actual phrases in 2009. The rise was notably pronounced amongst bigger economies, each creating and developed: 16 of the 19 states within the G20 noticed real-terms will increase in navy spending in 2009.
For a lot of in Western Europe or USA on the top of the monetary disaster, it could have been simple to neglect the international
monetary disaster, was primarily a Western monetary disaster (albeit with international reverberations). So this helps explains partly why navy spending didn’t fall as instantly as one would possibly in any other case assume. As SIPRI explains:
- Some nations like China and India haven’t skilled a downturn, however as an alternative loved financial progress
- Most developed (and a few bigger creating) nations have boosted public spending to deal with the recession utilizing massive financial stimulus packages. Army spending, although not a big a part of it, has been a part of that basic public expenditure consideration (some additionally name this
Army Keynesianism
- Geopolitics and strategic pursuits are nonetheless elements to venture or preserve energy:
rising navy spending for the USA, as the one superpower, and for different main or intermediate powers, akin to Brazil, China, Russia and India, seems to symbolize a strategic alternative of their long-term quest for international and regional affect; one which they could be loath to go with out, even in onerous financial occasions
, SIPRI provides.
For USA’s 2012 navy expenditure, for instance, though there may be fall, it’s primarily associated to war-spending (Iraq and Afghanistan operations primarily). However the baseline protection finances, by comparability, is basically just like different years (marking a discount within the price of elevated spending).
In contrast, on the subject of smaller nations — with no such energy ambitions and, extra importantly, missing the assets and credit-worthiness to maintain such massive finances deficits — many have in the reduction of their navy spending in 2009, particularly in Central and Jap Europe.
(Perlo-Freeman, Ismail and Solmirano, pp.1 – 2)
Pure assets have additionally pushed navy spending and arms imports within the creating world. The rise in oil costs means extra for oil exporting nations.
The pure useful resource curse
has lengthy been acknowledged as a phenomenon whereby nations, regardless of ample wealthy assets, discover themselves in battle and rigidity because of the energy struggles that these assets convey (inside and exterior influences are all a part of this).
Of their earlier 2006 report SIPRI famous that, Algeria, Azerbaijan, Russia and Saudi Arabia have been capable of improve spending due to elevated oil and fuel revenues, whereas Chile and Peru’s will increase are resource-driven, as a result of their navy spending is linked by legislation to earnings from the exploitation of key pure assets.
Additionally, China and India, the world’s two rising financial powers, are demonstrating a sustained improve of their navy expenditure and contribute to the expansion in world navy spending. In absolute phrases their present spending is barely a fraction of the USA’s. Their will increase are largely commensurate with their financial progress.
The navy expenditure database from SIPRI additionally exhibits that whereas proportion will increase over the earlier decade could also be massive for some nations, their total spending quantities could also be diversified.
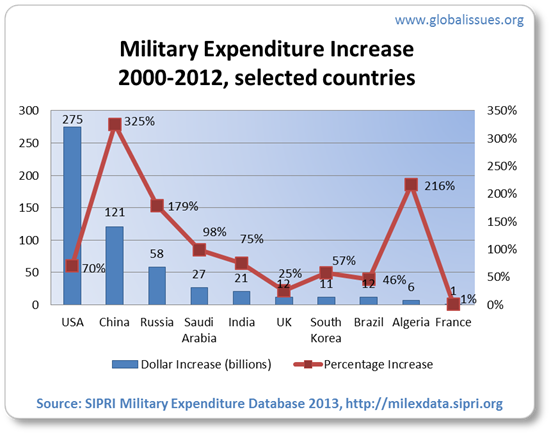
(See additionally this abstract of current tendencies, additionally from SIPRI. The newest figures SIPRI makes use of are from 2012, and the place mandatory (e.g. China and Russia), embody estimates.)
[ad_2]


